Testicular Pain: Care Instructions
Overview
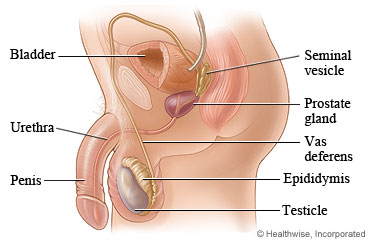
Pain in the testicles can be caused by many things. These include an injury to your testicles, an infection,
and testicular torsion.
Injuries and genital problems most often happen during sports or recreational activities, at work, or in a
fall. Pain caused by an injury usually goes away quickly. There is usually no long-term harm to your
testicles.
Infections that may cause pain include:
-
An infection of the testicles. This is called orchitis.
-
An abscess in the scrotum or testicles.
-
Some sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
-
A swelling of the tube attached to a testicle. This swelling is called epididymitis. It can cause pain and
is sometimes caused by an infection.
Testicular torsion happens when a testicle twists on the spermatic cord. This cuts off the blood supply to
the testicle. This is an emergency that often requires immediate surgery.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all
appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results
and keep a list of the medicines you take.
How can you care for yourself at home?
-
Rest and protect your testicles and groin. Stop, change, or take a break from any activity that may be
causing your pain or soreness.
-
Put ice or a cold pack on the area for 10 to 20 minutes at a time. Put a thin cloth between the ice and
your skin.
-
Wear briefs, not boxers. Briefs help support the injured area. You can use snug underwear or compression
shorts if it helps relieve your pain.
-
If your doctor prescribed antibiotics, take them as directed. Do not stop taking them just because you
feel better. You need to take the full course of antibiotics.
-
Ask your doctor if you can take an over-the-counter pain medicine, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol),
ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or naproxen (Aleve). Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on
the label.
-
If the doctor gave you a prescription medicine for pain, take it as prescribed.
When should you call for help?
 Call your
doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
Call your
doctor now or seek immediate medical care if:
Watch closely for changes in your health, and be sure to contact your doctor if:
Current as of: November 15, 2023
Content Version: 14.0
Care instructions adapted under license by your
healthcare professional. If you have questions about a medical condition or this instruction, always ask
your healthcare professional. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of
this information.